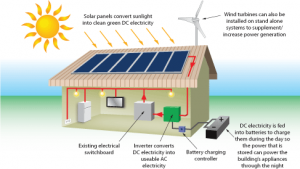
Solar PV systems use cells to convert sunlight into electricity. The PV cell consists of one or two layers of a semi conducting material, usually silicon. When light shines on the cell it creates an electric field across the layers causing electricity to flow. The greater the intensity of the light, the greater the flow of electricity.
PV cells are referred to in terms of the amount of energy they generate in full sunlight; know as kilowatt peak or kWp.
The electricity generated by PV solar cells is DC (direct current). The electricity used in your house is AC (alternating current). The current from the solar panel system has to go through an inverter, to convert it from DC to AC before it can be pumped into your house and used to run appliances.
Solar PV can be installed on new domestic dwellings, for Part L of new building regulations, retrofitted on existing dwellings and on commercial buildings to reduce their energy usage from the grid and also lowering C02 emissions.
Grants are now available for SEAI for the installation of PV panels into homes build before 2011. You will find more information on our grants page.

